Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
From Learning and training wiki
| Problem-Based Learning is a student-centered pedagogy in which students are challenged to learn through solving complex and realistic problems. Students construct their knowledge in a social context and are encouraged to organize and direct their learning process. The method claims to increase student motivation, activate prior knowledge, inspire creative thinking, facilitate the application of knowledge, and develop critical, collaborative, analytic, reasoning, problem-solving, self-monitoring, independent learning, decision-making, networking and communication skills. [1] See also: Constructivism, Cooperative Learning, Critical Incident-Based Learning, Design-Based Learning,Experiential Learning, Inquiry-Based Learning, Scenario-Based Learning, Social Constructivism, |
|
Role of the instructor
Role of the students
Tips for creating strong problems
Principles for assessment
Step by Step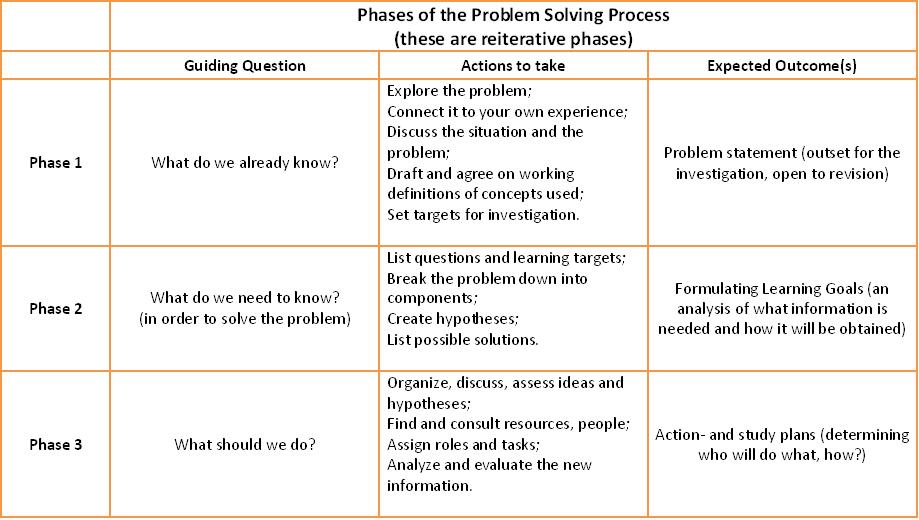 |
Job Aid
![]() Guidelines for Creating a PBL Course
Guidelines for Creating a PBL Course
| Find below additional information and resources. |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| PBL Rubric | Example rubric for grading problem based learning assignments. |
| Collaboration Rubric 1 | Collaboration rubric for e-learning. |
| Collaboration Rubric 2 | Collaboration rubric for self- and peer assessment. |
| Resource List | An extensive list of articles outlining application of PBL in multiple disciplines |
| PBL for E-learning | A brief gudie to problem based learning for synchronous e-learning. |
| PBL Online - A Case Study | Problem-Based Learning in an e-Learning Environment: A Case Study at Griffith University School of Medicine. |
| E-learning and PBL Report | E-Learning Tools and Problem Based Learning Seminar Report. |
| PBL Presentation Part 1 (Video, 6 mins) | Interesting video presentation giving an overview of and explaining the main concepts of Problem-Based Learning. |
| PBL Presentation Part 2 (Video, 7 mins) | The second part of the interesting video presentation detailing problem solving strategies, illustrated with examples. |
| PBL Presentation Part 3 (Video, 5 mins) | The final part of the interesting video presentation introducing pedagogical strategies using problem solving techniques. |
| Rubistar | Free online rubric creating application. |
References
- ↑ Rapid Instructional Design, Learning ID Fast and Right. George M. Piskurich, 2006, www.en.wikipedia.org (29 July 2011), www.udel.edu (29 July 2011), www.studygs.net (29 July 2011), www.sfsu.edu (29 July 2011), www.acs.edu.au (29 July 2011), www.edutechwiki.unige.ch (29 July 2011), www.adelaide.edu.au (29 July 2011)