Difference between revisions of "Evaluation"
From Learning and training wiki
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | '''See also''': [[A.D.D.I.E Model]] | + | '''See also''': [[A.D.D.I.E Model]], [[Formative Evaluation]] |
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 11:51, 5 November 2013
| Is an in-depth study which takes place at a discrete point in time, and in which recognized research procedures are used in a systematic and analytically defensible manner to form a judgment on the value of an intervention. It is an applied inquiry process for collecting and synthesizing evidence to produce conclusions on the state of affairs value, merit worth significance or quality of programmes, projects, policy, proposal or plan.[1]
Conclusions arising from an evaluation encompass both an empirical aspect (that something is the case) and a normative aspect (judgment about the value of something). The value feature in evaluation differentiates it from other types of inquiry such as investigative journalism or public polling for instance.
|
|
'Evaluation Questions:'
To what extent does the design and delivery of e-learning contribute or impede participants' learning and transfer of training to the job as compared with the design and delivery of face to face classroom based training? Key evaluation questions are not the same as survey questions for the evaluation in that they are broader and more comprehensive than specific questions used in a data collection tool. They may be useful in determining the type of questions to be asked in a data collection effort.[10]
Evaluation Tools:
Flow chart to determine if Level 2 evaluation is required [[3]] Steps for conducting Level 1 Training Evaluation (for UNITAR training events) [[4]] |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| DoView Software | DoView is an innovative software which lets you use a visual approach to monitor, evaluate and communicate your outcomes. |
References
- ↑ Fournier M. Deborah in Mathison, Sandra. Encyclopaedia of Evaluation, pp 138, Ed. University of British Columbia. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2005.
- ↑ Office of Internal Oversight Services (OIOS). Monitoring, Evaluation and Consulting Division, 2006.
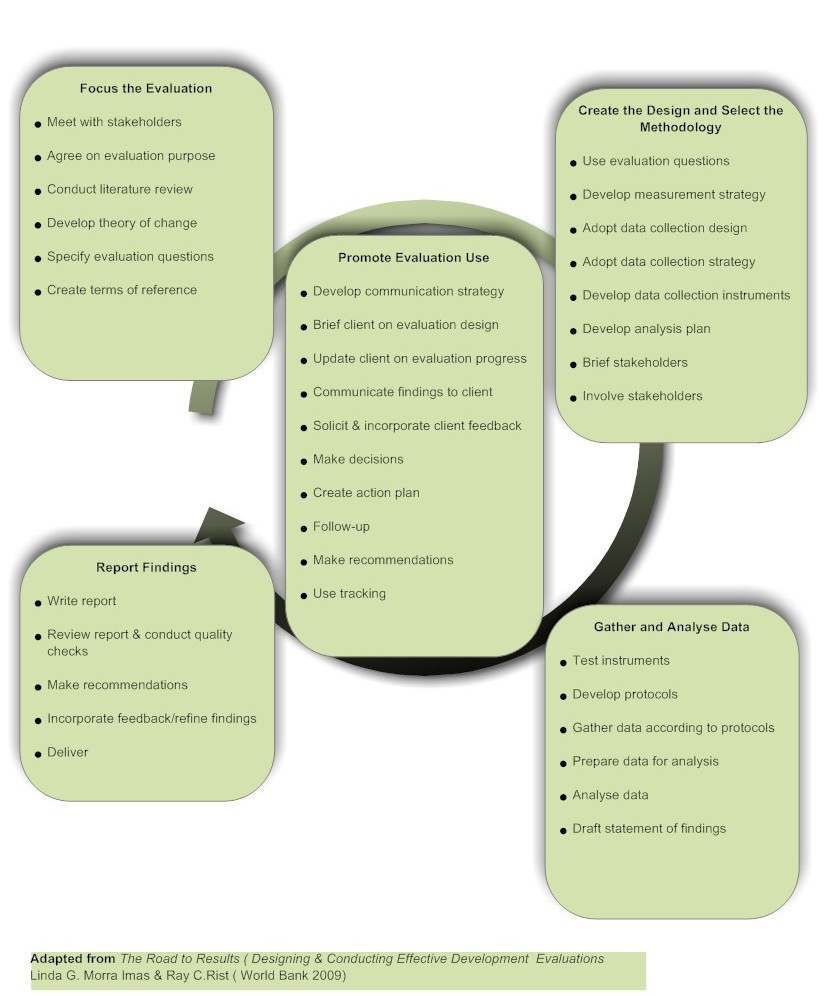
- ↑ Imas Linda G. Morra, Rist C. Ray. The Road To Results; Designing and Conducting Effective Development Evaluations pp 240. The World Bank, Washington DC, 2009.
- ↑ Smith M. F. in Mathison, Sandra. Encyclopaedia of Evaluation, pp 345, Ed. University of British Columbia. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2005.
- ↑ Gustafson, K. L., & Branch, R. B. Survey of instructional development models. 3rd ed. Syracuse, 1997.
- ↑ Kirkpatrick, D. L. Techniques for evaluating training programs. Journal of the American Society of Training Directors, 13, 3-26, 1959.
- ↑ Worthen, B. R., & Sanders, J. R. Educational evaluation. New York: Longman, 1987.
- ↑ Fitz-Enz, J. Yes…you can weigh training’s value. Training, 31(7), 54-58, July, 1994.
- ↑ Bushnell, D. S. Input, process, output: A model for evaluating training. Training and Development Journal, 44(3), 41-43, March, 1990.
- ↑ Russ-Eft F. Darlene in Mathison, Sandra. Encyclopaedia of Evaluation, pp 355, Ed. University of British Columbia. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2005.