Difference between revisions of "Learning Objectives"
From Learning and training wiki
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
=='''Job Aids'''== | =='''Job Aids'''== | ||
| − | [[Image:pdf.png]] [[Media: | + | [[Image:pdf.png]] [[Media:Learning_Objectives.pdf|Developing Learning Objectives]] |
[[Image:word.png]] [[Media:Learning_Objectives_Template_w.doc|Learning Objectives Workshops' Template]] | [[Image:word.png]] [[Media:Learning_Objectives_Template_w.doc|Learning Objectives Workshops' Template]] | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 31 August 2012
| Clear statement about the outcome of a training course, which informs what the trainee will be able to do or know after the training. They are presented from the trainee’s perspective, expressing as a target the improvement of competencies, which will enhance job performance. The performance signals to the trainees what must be done or learned in very specific terms.
The learning objectives are the starting point of the development of a learning activity. They constitute an essential element in the preparation of a training course. Defining adequate learning objectives can be one of the most time-consuming tasks in training design. Even though they may be expressed in a single paragraph of a few lines, they are the foundation of any training course as they relate to the overall training goal. Characteristics:
The initial statement (or bullet list) of the course learning objectives constitutes the primary objectives (First Level). These first level objectives may have other objectives subordinated to them (Second Level Objectives), which are supporting or enabling objectives. The First Level Objectives give the trainees an overall guide to what they will accomplish in the course whereas the Second Level Objectives are more content specific, telling exactly what they need to do. First and second level objectives are particularly used when the course content is divided into modules or units. Thus, there will be an overall objective for the course (First Level) and other subordinated objectives in each of the modules/units (Second Level) that support and directly enable the achievement of the overall course objective. In case modules/units are further divided into sections, these sections will also have learning objectives (third level), which are even more specific than the ones in the previous levels. [1]See also: A.D.D.I.E Model, Assessment, Bloom's Taxonomy, Instructional Design (ID) |
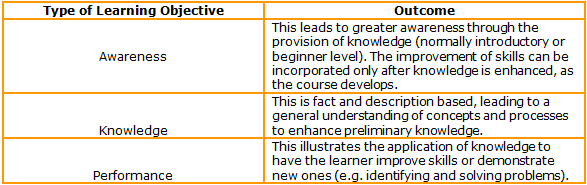
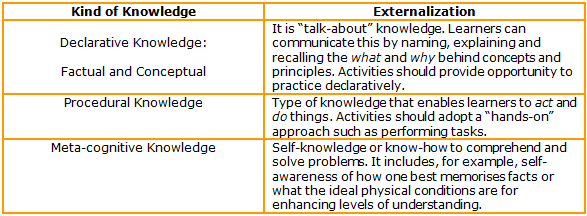
General Guidelines1. Determine whether the training is intended for developing awareness, enhancing knowledge or developing skill: 2. Identify the kind of knowledge learners will acquire: 3. Determine what knowledge, skills and attitudes trainees will develop by asking the following questions:
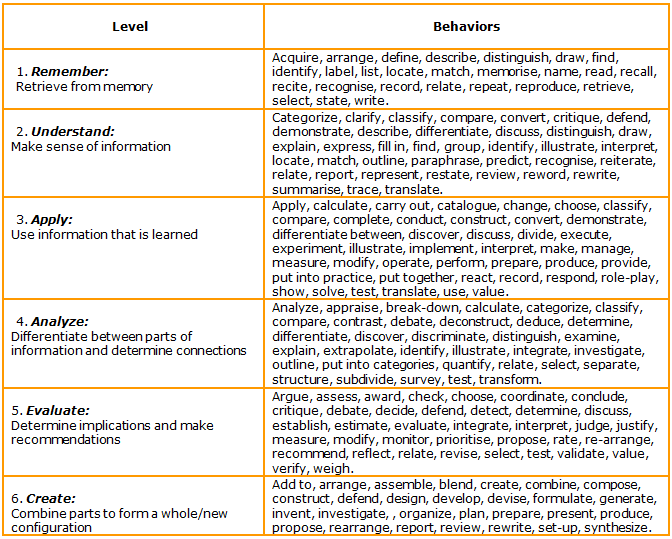
The answer will determine the type of objectives that must be developed, indicating the modalities of assessments that need to be designed. If the training course is an awareness raising, knowledge based and skills-based one it needs objectives stating each one of these components and assessments must be designed accordingly. 4. Start the statement with “At the end of the training the trainee will be able to” so as to make sure the objective makes sense from the trainee’s point of view. 5. Decide on the correct behaviors. What you choose in the form of behaviors is what the trainee must exhibit to master the objectives, which represent the performance to be achieved. 6. Include the behavioral part of the objective. Use action verbs with observable behavioral meaning. The action of each objective is what determines whether it is verifiable. 7. Use the list of behaviors categorized according to Bloom’s Taxonomy. Bloom’s taxonomy presents a system of classifying intellectual behavior that is important to learning as it provides a framework to be used when deciding which training component will add value. There are three categories: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Cognitive learning, which has to do with factual knowledge, is the category within which most training courses are developed. Bloom’s taxonomy categorizes knowledge in six progressively complex levels (from simple to more complex) which facilitate the construction of learning objectives: 8. Avoid using unverifiable verbs. Know and understand are wrongly used quite frequently. Whenever the action is inside the trainee’s head, the performance component of the objective is not verifiable. Learning can only be tested if it can be verified by the senses[2] Some verbs that are not observable and which should not be used to develop objectives are: appreciate; be aware of; comprehend; enjoy; know; know how to; learn; like; think about; understand. 9. Match the identified behaviors with adequate assessment activities. The type of assessment activity varies according to the behaviors expressed in each objective as they must match each one of them to allow proper evaluation. 10. Analyze if you have constructed a SMART objective:
Quick CheckWhen writing learning objective statements, ask yourself the following questions:
|
Job Aids
![]() Developing Learning Objectives
Developing Learning Objectives
![]() Learning Objectives Workshops' Template
Learning Objectives Workshops' Template
![]() Learning Obectives Courses' Template
Learning Obectives Courses' Template
| The following documents contain examples of learning goals and objectives developed according to the instructions: |
| General learning goals and objectives developed for different courses outside UNITAR. | |
| Learning objectives developed for UNITAR course on Urban Sanitation. | |
| Learning objectives developed for UNITAR / UNDP course on Democratic Governance. |
| Below you have the link to further resources which deal with some of the concepts related to learning objectives: |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| Assessments in e-Learning | This slideshow presents some of the basic concepts related to the development of good learning objectives and to the importance of measuring learning. It also presents different type of assessment. |
| Why learning goals are necessary for success? (Video, 5 min) | Watch this short 5 minute video, and learn about learning goals and how they can improve your instruction. |
| Learning and Retention: How to Improve Content Retention in Training (Video, 3 min) | The content is meant to help instructors question whether they are setting up their courses for short term or long term results. It discusses content retention strategies and the drawbacks of only teaching for short term retention. This video touches on the importance to think about training for long term memory retention. |
References
- ↑ www.depts.washington.edu(18 March 2008), www.utmem.edu(18 March 2008); Hassel-Corbiell, Ribes, Developing Training Courses: a technical writer’s guide to instructional design and development, Learning Edge Publishing, 2006; Phillips, Jack J. & Stone, Ron D., How to Measure Training Results, McGraw-Hill, 2002; Piskurich, George M., Rapid Instructional Design – Learning ID Fast and Right, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2006; Reiser, Robert A. & Dempsey, John V., Trends and Issues in Instructional Design and Technology, Pearson Prentice Hall, 2007; Stolovitch, Harold D. & Keeps, EricaJ., Telling Ain’t Training, ASTD Press, 2002. Woolcock, Michael J.V., Constructing a Syllabus, The Harriet Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning, Brown University, 2006.
- ↑ Hassel-Corbiell, Ribes, Developing Training Courses: a technical writer’s guide to instructional design and development, Learning Edge Publishing, 2006.
- ↑ http://capacitydevelopmentindex.pbworks.com, http://www.ucdenver.edu, http://www.celt.mmu.ac.uk, https://sites.google.com, http://www.wcu.edu, http://www.celt.iastate.edu (30 July 2012)