Difference between revisions of "Assessment"
From Learning and training wiki
| (5 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Term|ASSESSMENT|A generic term used to describe any systematic method e.g. quizzes, tests, surveys and exams, whose purpose is to evaluate and measure learners’ knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes by collecting, selecting, analyzing and interpreting the information obtained through performance observation. | + | {{Term|ASSESSMENT|A generic term used to describe any systematic method, e.g., quizzes, tests, surveys and exams, whose purpose is to evaluate and measure learners’ knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes by collecting, selecting, analyzing and interpreting the information obtained through performance observation. |
Learning and assessments are correlated since the learning tasks stimulate the development of some competencies/skills/abilities and the assessment makes learners demonstrate their achievement.<ref> [http://serc.carleton.edu serc.carleton.edu ](15 April 2008), [http://www.ltscotland.org.uk www.ltscotland.org.uk](15 April 2008)</ref> | Learning and assessments are correlated since the learning tasks stimulate the development of some competencies/skills/abilities and the assessment makes learners demonstrate their achievement.<ref> [http://serc.carleton.edu serc.carleton.edu ](15 April 2008), [http://www.ltscotland.org.uk www.ltscotland.org.uk](15 April 2008)</ref> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*Identify learning objectives; | *Identify learning objectives; | ||
| − | * | + | *Design and build assessments; |
*Design and build content and activities; | *Design and build content and activities; | ||
*Conduct [[Formative_Evaluation|formative evaluation]]; | *Conduct [[Formative_Evaluation|formative evaluation]]; | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
=='''Job Aid'''== | =='''Job Aid'''== | ||
| − | [[Image:pdf.png]] [[Media:Toolkit_Assessment. | + | [[Image:pdf.png]] [[Media:Toolkit_Assessment.pdf|General Guidelines for Developing Assessments.pdf]] |
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
| − | {{Addlink|}} | + | {{Addlink|Below you have a list of selected websites where you can find additional information:}} |
{|border=1; width= 100% | {|border=1; width= 100% | ||
!Link | !Link | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
|[http://www.edutopia.org/comprehensive-assessment-overview-video Performance assessments] | |[http://www.edutopia.org/comprehensive-assessment-overview-video Performance assessments] | ||
|Video explaining performance assessments approach in evaluating what students know and can do. | |Video explaining performance assessments approach in evaluating what students know and can do. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://capacitydevelopmentindex.pbworks.com/f/WBI_Learning+Design+Model.pdf WBI Learning Design Process] | ||
| + | |This document contains the learning design process illustrated by the Word Bank Institute. Five main steps for learning design are identified, going from the definition of outcomes and objectives, to the identification of methods, the selection of tools, the assembling of the programme and finally the evaluation of the tool. For each of these fundamentals steps, additional information is provided. A specific section is dedicated to identifying methods for assessing learners' knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://anethicalisland.files.wordpress.com/2013/05/event82.png Assessment Time, Infographic] | ||
| + | |How do you assess your students' performance? Was the assessment of the performance reliable and valid? Follow these 27 tips to reliably and validly assess the performance. | ||
|} | |} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:52, 5 November 2013
| A generic term used to describe any systematic method, e.g., quizzes, tests, surveys and exams, whose purpose is to evaluate and measure learners’ knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes by collecting, selecting, analyzing and interpreting the information obtained through performance observation.
Learning and assessments are correlated since the learning tasks stimulate the development of some competencies/skills/abilities and the assessment makes learners demonstrate their achievement.[1] There are five different styles of assessments which have different purposes as described below: Diagnostic Assessments: identify the needs and prior knowledge of learners with the purpose of directing them to the most appropriate learning experience. Pre-learning assessments (pre-tests, placement tests, personality assessments) Formative Assessments: strengthen memory recall providing practice for search and retrieval from memory, correct misconceptions and promote confidence in learners’ knowledge. Practice tests and exams (quizzes during learning, self assessment of knowledge, skills, attitudes) Needs Assessments: determine the needs or "gaps" between learners’ current and desired conditions to improve present performance or to correct a deficiency. Needs Analysis Surveys Reaction Assessments: determine the satisfaction level with a learning or assessment experience. Course evaluation Surveys, Employee Opinion Surveys, Customer/Partner satisfaction Surveys Summative Assessments: measure or certify knowledge, skills and aptitudes. Post Course Tests, Exams during study, Internal Exams, Open Exams, Licensing Exams, Pre-Employment Tests[2] See also: A.D.D.I.E Model, Assessment Standardization; Peer-to-Peer Assessment; Performance Assessment; Formative Evaluation; Instructional Design (ID); Learning Objectives; Summative Evaluation |
|
Good assessments correspond to well-written learning objectives. The following list shows how early in the instructional process they should be designed:
Design and build assessments
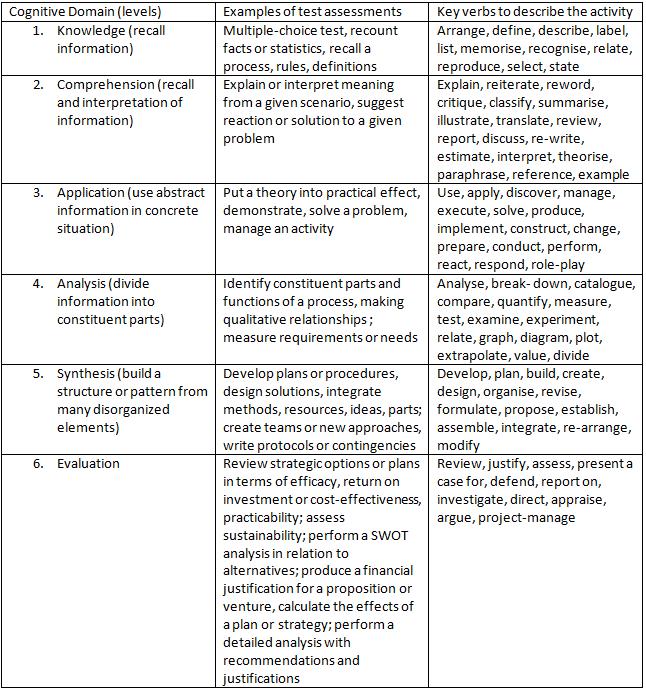
If the objective is a knowledge objective which calls for recalling or selecting, test items can be used. Below is a list[4] based on Bloom’s Taxonomy matching cognitive objectives with appropriate test assessments:
- Common sense cut-off (considering the lowest level of acceptable performance); - Percentage of total (identifying a passing grade for the entire assessment and a minimum grade for each learning objective in the task. Typically learners must pass both in order to pass the assessment. This choice is selected when a learning objective is more important than others).
|
Job Aid
![]() General Guidelines for Developing Assessments.pdf
General Guidelines for Developing Assessments.pdf
| Document | Content |
|---|---|
| Writing Questions for Training Programmes written by Bryan Hopkins | General principles for writing good and effective questions for training programmes. |
| Below you have a list of selected websites where you can find additional information: |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| Assessments in e-Learning | This slideshow presents some of the basic concepts related to the development of good learning objectives and to the importance of measuring learning. It also presents different types of assessment. |
| Developing powerful Training Assessments | Video about what to consider when performing assessments in training and teaching. It also describes what a powerful assessment is and why it is important in instructional design. |
| How Should We Measure Student Learning? The Many Forms of Assessment | Article stating the different existing forms of measuring students' abilities. |
| Performance assessments | Video explaining performance assessments approach in evaluating what students know and can do. |
| WBI Learning Design Process | This document contains the learning design process illustrated by the Word Bank Institute. Five main steps for learning design are identified, going from the definition of outcomes and objectives, to the identification of methods, the selection of tools, the assembling of the programme and finally the evaluation of the tool. For each of these fundamentals steps, additional information is provided. A specific section is dedicated to identifying methods for assessing learners' knowledge, skills, abilities and attitudes. |
| Assessment Time, Infographic | How do you assess your students' performance? Was the assessment of the performance reliable and valid? Follow these 27 tips to reliably and validly assess the performance. |
References
- ↑ serc.carleton.edu (15 April 2008), www.ltscotland.org.uk(15 April 2008)
- ↑ Shepherd, E., Godwin J., “Assessments through the learning process”, QuestionMark White Paper, 2010, pp. 3-9.
- ↑ Patti Shank, Develop valid assessments, Infoline December 2009, ASTD Press, p. 2
- ↑ www.businessballs.com (10 November 2011)