SWOT Analysis
From Learning and training wiki
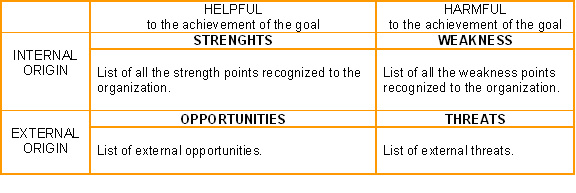
| A tool that identifies the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of an organization. Specifically, SWOT is a basic, straightforward model that assesses what an organization can and cannot do as well as its potential opportunities and threats. The SWOT analysis takes the information from an environmental analysis and separate it into internal (strengths and weaknesses) and external issues (opportunities and threats). Once this is completed, the SWOT analysis determines what can be of assistance to the organization in accomplishing its objectives, and what obstacles must be minimized to achieve desired results. [1] |
|
Strengths and opportunities are identified as enhancers to desired performance, while weaknesses and threats are inhibitors.[2]
Step by Step
SWOT MatrixJob Aids |
References
- ↑ www.answers.com (20 August 2008), www.netmba.com (20 August 2008), en.wikipedia.org (20 August 2008)
- ↑ www.businessballs.com (3 October 2008), web.worldbank.org
- ↑ www.quickmba.com (13 August 2008), Wikipedia (13 August 2008), Project Cycle Management Guidelines, European Commission, 2004