Difference between revisions of "Mind Mapping"
From Learning and training wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Term|MIND MAPPING|A [[Learning Methodologies|Learning methodology]] that consists of drawing [[diagrams]] | + | {{Term|MIND MAPPING|A [[Learning Methodologies|Learning methodology]] that consists of drawing [[diagrams]] to represent words, ideas, tasks, processes or other issues. It is a non-linear way of organizing information and a technique that allows to capture the natural flow of ideas about a central topic. Each idea or fact is written down and then linked by lines or curves to its major or minor (following or previous) idea or fact, thus creating a web of relationships. Its purpose is to focus attention, capturing and framing knowledge to facilitate the sharing of ideas and concepts. |
Mind maps can be used to: | Mind maps can be used to: | ||
*Summarize information | *Summarize information | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 10 October 2008
| A Learning methodology that consists of drawing diagrams to represent words, ideas, tasks, processes or other issues. It is a non-linear way of organizing information and a technique that allows to capture the natural flow of ideas about a central topic. Each idea or fact is written down and then linked by lines or curves to its major or minor (following or previous) idea or fact, thus creating a web of relationships. Its purpose is to focus attention, capturing and framing knowledge to facilitate the sharing of ideas and concepts.
Mind maps can be used to:
|
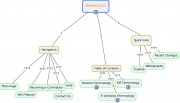
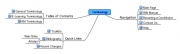
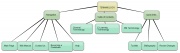
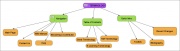
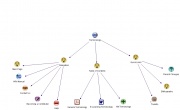
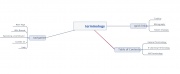
| In the table below there is a list of mindmapping tools. All of them are free-sources. You will also find some basic information about them, like if they are downoladable or on-line application, what kind of features and which degree of freedom in constructing the map they offer. By clicking the visualization image you will be able to see a sample map. |
| Tools | Type of Application | Special Features | Structure | Visualization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freemind | To download
(1,51 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure. | |
| CMAP Tools | To downlad
(1,62 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure. Every arrow connecting two nodes is supposed to contain a label | |
| Mindmeister | On-line. Two versions: Basic for free,
Premium to pay (4$ per month) |
Link to files and web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure. | |
| Bubbl.us | On-line | Link to web-sites, impossible to link files | Free structure | |
| VUE | To download
(1,51 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure. Possibility two add a label on the connection between two nodes. | |
| Compendium | To download
(1,58 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure. Every node has to belong to a cathegory (question, decision, argument, idea..) | |
| Wisemapping | On-line | Link to web-sites, impossible to link files | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure. | |
| Mind42 | On-line | Link to web-sites, impossible to link files | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure. |
References
- ↑ astd-cac.net (08 July 2008) Wikipedia(08 July 2008) www.mind-mapping.co.uk (08 July 2008), www.illumine.co.uk (08 July 2008), www.mindtools.com (08 July 2008), www.thinksmart.com (8 October 2008), www.businessdictionary.com (8 October 2008)