Results-Oriented Job Description
From Learning and training wiki
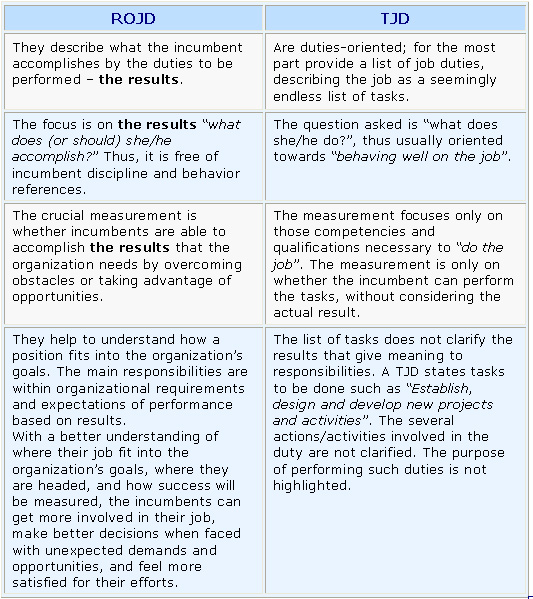
Understanding the differences between ROJD and TJDWhat's in it for you in a Result-Oriented Job Description?
|
| Step 1
Job Purpose |
The overall job purpose is the mission of the position within the organization. Explain why the position exists within the organization, identifying the main customers served by the incumbent, and connect the position to relevant outcomes. Each incumbent enhances the organization’s mission by a combination of essential responsibilities, which can be defined by one broad, all encompassing phrase.
Example: Sales and Marketing Executive: To plan and carry out direct marketing and sales activities, so as to maintain and develop sales of SNP ABC machinery range to UK major accounts and specifiers, in accordance with agreed business plan. In this section explain also where the position is located within the organizational structure, who supervises and/or gives work direction to the position, and what positions the incumbent supervises (if applicable). |
| Step 2
List of Tasks |
Dedicate some time in this step. It will facilitate your way through the next one, normally more complicated.
Example: Clarify customer complaint; determine the cause of the problem; select and explain the best solution to solve the problem; expedite correction or adjustment; follow up to ensure resolution – are all tasks that potentially can be grouped together under a heading. |
| Step 3
The Essential Responsibilities |
In step 2 you have :
Step 3 is the most difficult part. This step shifts the focus of the work from the tasks to be performed into the expected results. You have to identify the set of essential responsibilities of the job. Essential responsibility is a heading that describes an area of work that usually requires several individual tasks to be completed. An essential responsibility is what is to be accomplished (the result) in the specific way the organization wants: the tasks described – how the incumbent is expected to accomplish the results. DON’T: confuse the list of essential responsibilities with the individual tasks that must be performed to accomplish the essential responsibility (the result to be accomplished). To distinguish, ask and answer the following questions:
Think of the essential responsibilities of your job. A junior position will not need more than 8; a managerial position in a small organization might need 15 – but never more than this! The result will be a list with various headings of key responsibilities. Once various headings that describe results are developed, the tasks can be sorted logically under the appropriate essential responsibility. Help needed? Consult the group of tasks you produced in the previous step. As they were logically clustered you should easily identify a key responsibility where a group of tasks belong to. So:
Note: a key responsibility may require various tasks to be performed! |
| Step 4
The ROJD’s writing method |
You have to describe each essential responsibility with a results-by-task three-four-line formula – the Results Statement – describing expectations for successful performance. They are the general statements of what the incumbent is intended to accomplish. They connect the intended outcome to the clients and provide a sound basis for structuring work and personal development plans.
The method of writing the results statement involves the use of the connector word “by”. The sentence starts with a general active verb stating the result. It is then followed by the specific tasks to be performed (what must be done to achieve the desired result). Thus, the verbs describing the tasks appear all in “ing” form. Changing verbs from passive to active clarifies the job function. It demonstrates that accomplishing each essential responsibility (the result the organization desires) involves performing a series of tasks. Thus, the job function is elevated with a strong professional identity. The essential responsibilities must appear in order of importance. The sense of priority demonstrates to the incumbent what she/he should not do when put under time or other resource pressure. |
| Step 5
Putting it all together Examples |
A three-five-line structure with the essential responsibility in bold type, followed by the expected results, is the final product you need to get – the results statement:
Resolves product problems by clarifying customer complaint; determining the cause of the problem; selecting the best solution to solve the problem; expediting adjustment; following up to ensure resolution. Implement new projects to expand the organization’s portfolio by identifying new opportunities; providing technical guidance into priority activities; maintaining contacts with clients and stakeholders; assuring a service oriented approach to clients; Process information by reading incoming mail, obtaining background materials, highlighting important points, retrieving and attaching related documents, routing mail to concerned parties; drafting standard correspondence; filing documents. |
Job Aid |
|
Recommended Reading Profile of an Effective Manager – For managerial excellence in the United Nations, Office of Human Resources Management – Division for Organizational Development. |
References
- National Education Association, What is ROJD?, www.nea.org, 3 February 2009
- Article Base, Management Articles, How to write a Result-Oriented Job Description, www.articlebase.com, 3 February 2009
- Helium, Writing a job description that works for your employees, www.helium.com, 4 February 2009
- Business Balls, Writing Results-Oriented Job Descriptions, www.businessballs.com, 4 February 2009
- Some tips for writing a good job description, author unknown, circulated by Human Resources Section, February 2009
- Performance Evaluation, HR Memorandum, 21 September 2008
- Classification of Posts, HR Memorandum, 12 January 2009