Mind Mapping
From Learning and training wiki
| A learning methodology that consists of drawing diagrams to represent words, ideas, tasks, processes or other issues. It is a non-linear way of organizing information and a technique that allows to capture the natural flow of ideas about a central topic. Each idea or fact is written down and then linked by lines or curves to its major or minor (following or previous) idea or fact, thus creating a web of relationships. Its purpose is to focus attention, capturing and framing knowledge to facilitate the sharing of ideas and concepts.
Mind maps can be used to:
Originally mind maps were created on paper, normally spread over a wall where people could freely write down their ideas. Today there are several tools that allow the creation of electronic mind maps. They can be very helpful when one wants to modify an idea previously inserted or organize all the ideas in a different way or order. These electronic tools also allow that a group of people, working in different locations, contribute to the creation of mind map to address an issue of their interest. |
Step by Step
Practical Tips
|
Job Aid
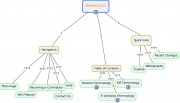
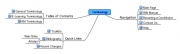
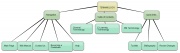
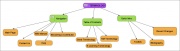
| Below you have a selected compilation of electronic tools that allow the creation of mind maps. All the tools listed are free, available on the Internet. For each tool listed some general information is provided : on-line or desktop use; special features available; and degree of flexibility when constructing the map. Click on the image on last column (visualization) to see a sample of the type of map each tool allows you to create.
|
| Tools | Type of Application | Special Features | Structure | Visualization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freemind | To download
(1,51 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| CMAP Tools | To download
(1,62 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure; but every arrow connecting two nodes must contain a label | |
| Mindmeister | On-line. Two versions: Basic for free,
Premium to pay (4$ per month) |
Link to files and web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| Bubbl.us | On-line | Link to web-sites | Free structure | |
| VUE | To download
(1,51 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure. Possibility two add a label on the connection between two nodes. | |
| Compendium | To download
(1,58 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure; but every node has to belong to a category (question, decision, argument, idea, etc.) | |
| Wisemapping | On-line | Link to web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| Mind42 | On-line | Link to web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| Freeplane | To download
(22,7 MB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure; a growing set of node extensions provide for details, metadata, images, hyperlinks. |
| Below is an additional resource for mind map templates and e-books:
|
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| Mind Map Inspiration | This resource provides access to a number of mind map templates. Additionally, links are available to some free e-books on using mind maps and a gallery of mind maps to browse through. |
| Mind mapping for instructional design | This article highlights the importance of Mind Mapping tools in playing an increasingly role in the design, planning and implementation of learning experiences. |
References
- ↑ astd-cac.net (08 July 2008) Wikipedia(08 July 2008) www.mind-mapping.co.uk (08 July 2008), www.illumine.co.uk (08 July 2008), www.mindtools.com (08 July 2008), www.thinksmart.com (8 October 2008), www.businessdictionary.com (8 October 2008)
- ↑ www.wikihow.com (10 October 2008), www.thinkingbusiness.co.uk (10 October 2008), www.mindtool.com (10 October 2008), Tools for Knowledge and Learning, odi, 2006