Blended Learning
From Learning and training wiki
|
Blended Learning is an integrated learning approach that combines traditional learning methods and media with modern e-Learning/computer-mediated tools. It seeks to integrate these methods and tools to enhance learning outcomes. A primary consideration is how to best bring together the social aspects of face-to-face communication with the flexibility and efficiency of e-Learning. Kinds of blended learning While the ways of combining e-Learning and face-to-face teaching practices are many, the nature of ‘the blending’ can be characterised in two ways: 1. Supplemental Blending: the incorporation of computer tools for delivering learning elements of a course without altering the structure of a traditional course. In other words, technology is used to enhance traditional instruction, most typically in the provision of course content and important information. E.g. Electronic/power point web notes in a university lecture (replacing text books); computer based quizzes/exams with written and multiple choice answers. 2. Replacement Blending: full integration of web-based computer tools and media into the instruction of a course, causing changes in structure and methodology which differ from traditional teaching methods. Such blending typically causes radical changes in the balance between face-to-face and virtual learning environments, and the nature of any face-to-face learning taking place. Replacement blending is an evolving concept, with continuous innovations in computer-based methodology. Some contemporary examples include:
|
|
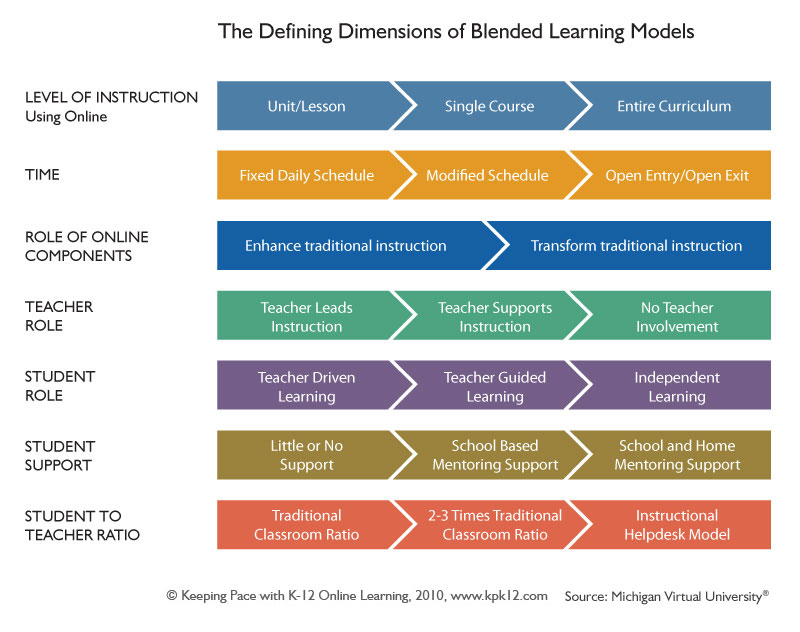
Dimensions There is no fixed method or technique for designing a blended learning course. However, the dimensions and major options to be considered for a teacher/trainer concerning the balancing and integrating traditional and computer-based learning approaches for a given course, can be summed up in the following model: All seven dimensions represent important components making up the framework of a given course. When planning their course, teachers must choose the most appropriate option for each dimension. There is no formula for doing this. Rather, teachers/trainers must consider the parameters of their education field – target group, teaching content, teaching and learning objectives, learning situation etc. – and their own preference/style, in order to make an informed judgement for each dimension. Furthermore, each dimension cannot be planned in isolation. Teachers must consider how each dimension integrates into an optimal whole. For example, a teacher may choose to have comprehensive course materials made available online for the ’Level of instruction’ dimension of their course. This would likely mean that a ‘Fixed Daily Schedule’, ‘Teacher Driven Learning’ and ‘Teacher Led instruction’ would be inappropriate. Instead giving students initiative to conduct ‘independent learning’, and allowing ‘open entry/exit’ for the timing in which students can access the learning materials, would integrate more effectively. On the other hand, if the ‘Role of the Online Components’ was only to ‘assist traditional instruction’ (instead of driving the learning), then a ‘fixed schedule’ and ‘teacher led instruction’ would be probably integrated more appropriately. Advantages and Disadvantages of different instructional forms The pros and cons of online vs. traditional forms of teaching depend on a teacher’s personal style, and the parameters of a given teaching context. However, some generic considerations concerning in class work vs. e-learning are provided below: In class Positives
Online/E-Learning Positives
Other points
Learning Management System The vast majority of blended learning programs, use a computer based class management platform, called a Learning Management System (LMS). This is a place where an administrator (or teacher) and students can interact for both learning, and administrative purposes. Common features include:
Increasingly, modern ‘blended learning’ courses look to incorporate new tools and media into their lessons, learning activities and assessments. By looking beyond traditional norms teachers and trainers aim to prepare their students for the use of modern technology in the demonstration of their learning. Common examples include:
|
| Below you have some links to resources and materials providing additional information about blended learning. |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| Filling the Gaps of Traditional Training | During this short training you can analyze the pros and cons of traditional training approaches and discover the benefits of a blended learning solution. You will identify key factors in choosing a learning solution and consider multiple options to meet learners’ needs. Although there’s no single formula for a “perfect” training program, this session can help you build unique and customized strategies. (Video; 14 minutes) |
| Estimating Project Scope Successfully | In this brief course you will examine some industry metrics for scoping different components of a blended solution. You will also discover tasks to perform when estimating a project, and you’ll learn how to estimate development time for newer technologies that so far don’t have established metrics. By the end of the course, you will have a good foundation for scoping unique and customized training strategies. (Video;9 minutes) |
| Blended Learning: How to Incorporate E-Learning into a Blended Classroom Model
(Video, 4 min) |
This 4 minute video gives advice on how to view e-learning as a supplementary resource that learners work on during their own time. Other tips in the video include discussing content review, assessments and when to fact check. |
| Man Versus Machine | An article that illustrates the benefits of blended learning and provides suggestions on how to make it more effective. The main aspects analyzed are: the content, which should be adapted to the media used in the course and made consistent across units and modalities, and the balance, which should be found between asynchronous and synchronous modalities as well as between knowledge acquisition and practical application. |
| Real Blended Learning Stands Up | An article that points out the benefits of blended learning and gives some examples of blended curricula as well as activities (e.g. role plays and games) that can be included in a blended learning programme. The article also illustrates the importance of enriching the learning process with a variety of learning methods in order to match different learning styles. |
| 11 steps of effective project-based learning in a blended classroom | An article that analyses student-to-material interactions as part of the blended learning model, specifically the process of project-based learning in a blended classroom. |
| What is Blended Learning? These videos will get you started | Videos from Edudemic reader Frederic Skrzypek shedding some light on the importance of Blended Learning. |
| Pinterest Board on Blended Learning
(Infographics) |
Check out Click4it's Pinterest Board on Blended Learning and discover more about Blended Learning! |
| Document | Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Blended learning: Uncovering its ransformative potential in higher education | The purpose of this paper is to provide a discussion of the transformative potential of blended learning in the
context of the challenges facing higher education. Based upon a description of blended learning, its potential to support deep and meaningful learning is discussed. From here, a shift to the need to rethink and restructure the learning experience occurs and its transformative potential is analyzed. Finally, administrative and leadership issues are addressed and the outline of an action plan to implement blended learning approaches is presented. The conclusion is that blended learning is consistent with the values of traditional higher education institutions and has the proven potential to enhance both the effectiveness and efficiency of meaningful learning experiences. |
Blended Learning Systems: Definition, Current Trends, and Future Directions | Article by Charles R. Graham. |
References
http://www.educause.edu/research-and-publications/books/learning-spaces/chapter-11-designing-blended-learning-space-student-experience (14 December 2012), http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integriertes_Lernen (14 December 2012), http://weblearning.psu.edu/blended-learning-initiative/what_is_blended_learning (14 December 2012), www.youtube.com/watch?v=UM_Y2NSJcmE (14 December 2012); http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blended_learning (14 December 2012); http://www.onlineprogramhowto.org/decisions/what-does-online-and-blended-learning-look-like/the-dimensions-of-online-and-blended-learning/ (14 December 2012).