Difference between revisions of "Brainstorming"
From Learning and training wiki
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
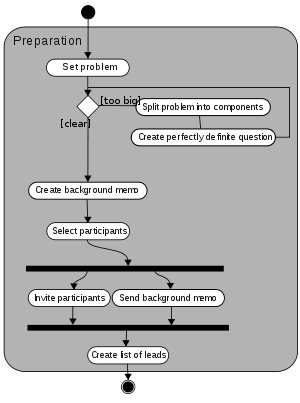
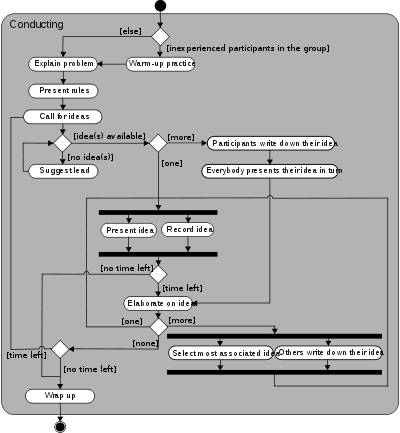
Although traditional brainstorming does not increase the productivity of groups (as measured by the number of ideas generated), it may still provide benefits, such as boosting morale, enhancing work enjoyment, and improving team work. Thus, numerous attempts have been made to improve brainstorming or use more effective variations of the basic technique. | Although traditional brainstorming does not increase the productivity of groups (as measured by the number of ideas generated), it may still provide benefits, such as boosting morale, enhancing work enjoyment, and improving team work. Thus, numerous attempts have been made to improve brainstorming or use more effective variations of the basic technique. | ||
| − | [[Image:Brainstorming_session.png]] | + | [[Image:Brainstorming_session.png]] .................................................................................................................................................................... |
....................... | ....................... | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 26 May 2009
| A group of problem-solving techniques used to generate a large number of ideas: each participant share different solutions
to solve a problem by rapidly generating a variety of possible solutions. A similar process undertaken by a person to solve a problem by rapidly generating a variety of possible solutions. creativity technique used to generate a large number of ideas for the solution of a problem. The method was first popularized in the late 1930s by Alex Faickney Osborn in a book called Applied Imagination. Osborn proposed that groups could double their creative output with brainstorming.[1] Although brainstorming has become a popular group technique, researchers have not found evidence of its effectiveness for enhancing either quantity or quality of ideas generated. Because of such problems as distraction, social loafing, evaluation apprehension, and production blocking, brainstorming groups are little more effective than other types of groups, and they are actually less effective than individuals working independently.[2][3][4] In the Encyclopedia of Creativity, Tudor Rickards, in his entry on brainstorming, summarizes its controversies and indicates the dangers of conflating productivity in group work with quantity of ideas.[5] Although traditional brainstorming does not increase the productivity of groups (as measured by the number of ideas generated), it may still provide benefits, such as boosting morale, enhancing work enjoyment, and improving team work. Thus, numerous attempts have been made to improve brainstorming or use more effective variations of the basic technique.
....................... [1] |