Difference between revisions of "SWOT Analysis"
From Learning and training wiki
Chantal joly (Talk | contribs) |
Chantal joly (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
#'''Threat''' : An external factor that has the potential to reduce an organization's performance. For example : political and environmental effects, market demand, IT developments. The aim of the Swot is to counter. | #'''Threat''' : An external factor that has the potential to reduce an organization's performance. For example : political and environmental effects, market demand, IT developments. The aim of the Swot is to counter. | ||
| − | '''Strengths'''and | + | '''Strengths'''and '''Opportunities'''are identified as enhancers to desired [[Performance|performance]], while '''Weaknesses''' and ''Threats'''are inhibitors.<ref>[http://www.businessballs.com www.businessballs.com] (3 October 2008), [http://web.worldbank.org web.worldbank.org]</ref> |
Revision as of 14:16, 13 October 2008
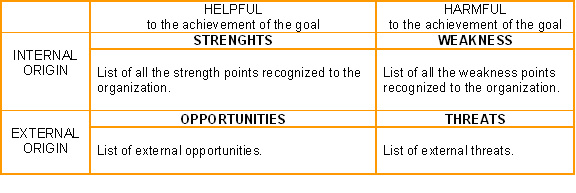
| A tool that identifies the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of an organization. Specifically, SWOT is a basic, straightforward model that assesses what an organization can and cannot do as well as its potential opportunities and threats. The SWOT analysis takes the information from an environmental analysis and separate it into internal (strengths and weaknesses) and external issues (opportunities and threats). Once this is completed, the SWOT analysis determines what can be of assistance to the organization in accomplishing its objectives, and what obstacles must be minimized to achieve desired results. [1] |
|
'Strengthsand Opportunitiesare identified as enhancers to desired performance, while Weaknesses and Threatsare inhibitors.[2]
SWOT Matrix
Step by Step
Job Aids |
References
- ↑ www.answers.com (20 August 2008), www.netmba.com (20 August 2008), en.wikipedia.org (20 August 2008)
- ↑ www.businessballs.com (3 October 2008), web.worldbank.org
- ↑ www.quickmba.com (13 August 2008), Wikipedia (13 August 2008), Project Cycle Management Guidelines, European Commission, 2004