Difference between revisions of "Logic Model"
From Learning and training wiki
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
A [[Performance|performance]] story based on a logical model does not only report evidence to support the casual chain but addresses the extent to which the outcomes can be attributed to the programme or project and the influence of external factors.<ref>McCawley F. Paul. The Logic Model for Program Planning & Evaluation. University of Idaho Extension, 2002.</ref><ref>Roges, J. Patricia in Mathison, Sandra. Encyclopaedia of Evaluation, pp 225, Ed. University of British Columbia. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2005.</ref> | A [[Performance|performance]] story based on a logical model does not only report evidence to support the casual chain but addresses the extent to which the outcomes can be attributed to the programme or project and the influence of external factors.<ref>McCawley F. Paul. The Logic Model for Program Planning & Evaluation. University of Idaho Extension, 2002.</ref><ref>Roges, J. Patricia in Mathison, Sandra. Encyclopaedia of Evaluation, pp 225, Ed. University of British Columbia. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2005.</ref> | ||
| − | See also: [[Outcome | + | See also: [[Outcome Mapping|Outcome Mapping]], [[Outcomes|Outcomes]].}} |
Revision as of 16:23, 6 January 2014
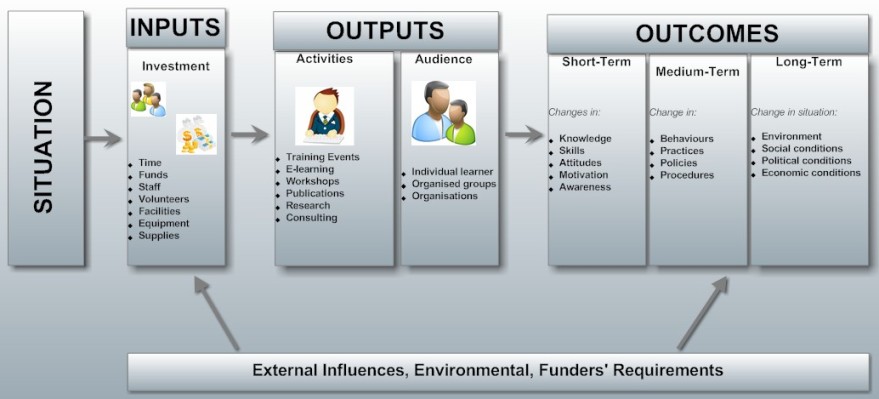
| Is an articulate model of how a project or programme is intended to contribute to its stated outcomes. A logic model can be a narrative or graphical depiction of a process that communicates the underlying assumptions upon which an activity is expected to lead to a specific result. It illustrate a sequence of cause-and-effect relationships - a systems approach to communicate the path toward a desired result and focuses on intermediate outcomes instead of specified processes.
Logical models are used prospectively for planned projects or programmes or retrospectively for existing ones and serve the following purposes:
A performance story based on a logical model does not only report evidence to support the casual chain but addresses the extent to which the outcomes can be attributed to the programme or project and the influence of external factors.[1][2] See also: Outcome Mapping, Outcomes. |
SIMPLE LOGIC MODEL