Difference between revisions of "Brainstorming"
From Learning and training wiki
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
#Aim to generate a large quantity of ideas, according to the assumption that it increases the probability to produce a fit solution to the problem (''quantity breeds quality''); | #Aim to generate a large quantity of ideas, according to the assumption that it increases the probability to produce a fit solution to the problem (''quantity breeds quality''); | ||
#Avoid judgement and criticism, since the negative thinking can demotivate some members of the group to contribute their ideas and, moreover, unusual perspectives often help to the effective solution; | #Avoid judgement and criticism, since the negative thinking can demotivate some members of the group to contribute their ideas and, moreover, unusual perspectives often help to the effective solution; | ||
| − | #Combine ideas by a process of association in order to improve them. | + | #Combine ideas by a process of association in order to improve them. |
[[Image:Brainstorming_session.png]] | [[Image:Brainstorming_session.png]] | ||
| − | + | ===Session conduct=== | |
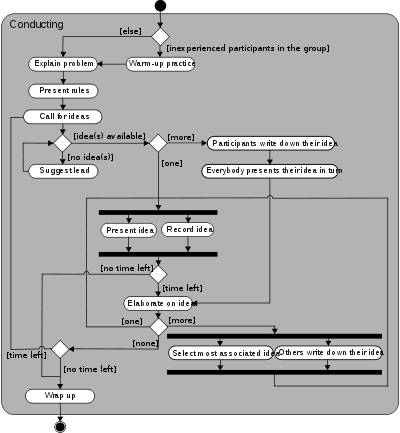
To lead a brainstorming session the facilitator usually follows these steps: | To lead a brainstorming session the facilitator usually follows these steps: | ||
#Warm-up, to make the participants feel in a criticism-free environment; | #Warm-up, to make the participants feel in a criticism-free environment; | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
#Organizing and clustering ideas; | #Organizing and clustering ideas; | ||
#Evaluating ideas in order to identify those worthy of action | #Evaluating ideas in order to identify those worthy of action | ||
| − | #Thanking the participants<ref> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brainstorming Wikipedia] (26 May 2009)</ref> | + | #Thanking the participants<ref> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brainstorming Wikipedia] (26 May 2009)</ref> |
| − | [[Image:Brainstorming_conduct.png]] | + | [[Image:Brainstorming_conduct.png]]}} |
Revision as of 17:00, 26 May 2009
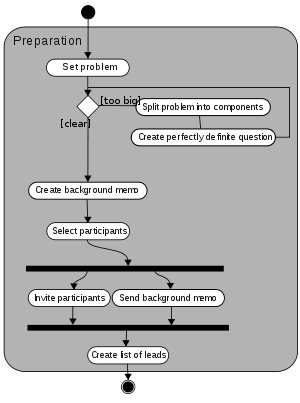
Group of creativity methods first popularized by A.F. Osborne in 1941, in which all member of a team are encouraged to generate and share ideas on a specific topic. The aim is to put the participants in the condition of creating original ideas and developing unusual approaches to a problem. Therefore, the group should feel free to express the ideas spontaneous just focusing on quantity, since every evaluation must be postponed later in the process. Following some ground rules in brainstorming can reduce the inhibitions in the group, including self-censorship, and enhance creative thinking:
Session conductTo lead a brainstorming session the facilitator usually follows these steps:
 |