Difference between revisions of "SWOT Analysis"
From Learning and training wiki
Chantal joly (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
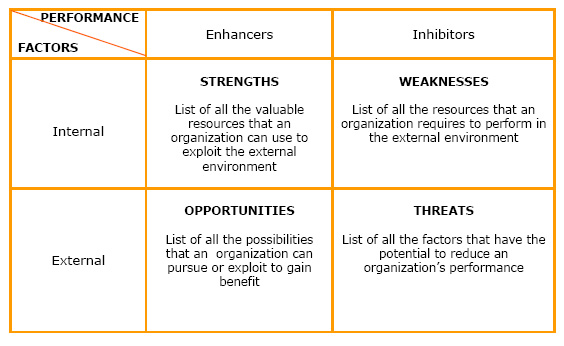
#'''Strengths''': Internal competences, valuable resources or attributes that an organization can use to exploit the external environment. For example: competitive advantages, resources, certifications, experience, management cover, communication. The aim of the SWOT is to maintain, build, and leverage. | #'''Strengths''': Internal competences, valuable resources or attributes that an organization can use to exploit the external environment. For example: competitive advantages, resources, certifications, experience, management cover, communication. The aim of the SWOT is to maintain, build, and leverage. | ||
| − | #'''Weaknesses''': Internal lack of competence, resources or attributes that an organization requires to perform in the external environment. For example: gaps in capabilities, reputation, financials, reliability of data. The aim of the SWOT is to remedy or exit. | + | #'''Weaknesses''': Internal lack of competence, resources or attributes that an organization requires to perform in the external environment. For example: gaps in capabilities, reputation, financials, and reliability of data. The aim of the SWOT is to remedy or exit. |
#'''Opportunities''': External possibilities that an organization can pursue or exploit to gain benefit. For example : market developments, competitors' vulnerabilities, information and research. The aim of the SWOT is to prioritize and optimize them. | #'''Opportunities''': External possibilities that an organization can pursue or exploit to gain benefit. For example : market developments, competitors' vulnerabilities, information and research. The aim of the SWOT is to prioritize and optimize them. | ||
| − | #'''Threats''': External factors that has the potential to reduce an organization's performance. For example : political and environmental effects, market demand, IT developments. The aim of the SWOT is to counter them. | + | #'''Threats''': External factors that has the potential to reduce an organization's performance. For example: political and environmental effects, market demand, IT developments. The aim of the SWOT is to counter them. |
'''Strengths''' and '''Opportunities''' are identified as enhancers to desired [[Performance|performance]], while '''Weaknesses''' and '''Threats''' are inhibitors.<ref>[http://www.businessballs.com www.businessballs.com] (3 October 2008), [http://web.worldbank.org web.worldbank.org]</ref> | '''Strengths''' and '''Opportunities''' are identified as enhancers to desired [[Performance|performance]], while '''Weaknesses''' and '''Threats''' are inhibitors.<ref>[http://www.businessballs.com www.businessballs.com] (3 October 2008), [http://web.worldbank.org web.worldbank.org]</ref> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
*Categorize all the SWOT factors into the [[#Job Aids|Matrix]] and work to build consensus around their placement. | *Categorize all the SWOT factors into the [[#Job Aids|Matrix]] and work to build consensus around their placement. | ||
*The situation is then analyzed with the objective of identifying ways in which the organization’s strengths can be built, upon to overcome the identified weaknesses, and opportunities can be taken to minimize threats. | *The situation is then analyzed with the objective of identifying ways in which the organization’s strengths can be built, upon to overcome the identified weaknesses, and opportunities can be taken to minimize threats. | ||
| − | *A strategy for making improvements is formulated and subsequently developed, using any planning tool. <ref>[http://www.quickmba.com www.quickmba.com] (13 August 2008), [http://www.wikipedia.org Wikipedia] (13 August 2008), Project Cycle Management Guidelines, European Commission, 2004</ref> | + | *A strategy for making improvements is formulated and subsequently developed, using any planning tool. <ref>[http://www.quickmba.com www.quickmba.com] (13 August 2008), [http://www.wikipedia.org Wikipedia] (13 August 2008), Project Cycle Management Guidelines, European Commission, 2004</ref>}} |
| − | =='''Job | + | =='''Job Aid'''== |
[[Image:word.png]] [[Media:Swot_Matrix_Template.doc|Swot Matrix Template]] | [[Image:word.png]] [[Media:Swot_Matrix_Template.doc|Swot Matrix Template]] | ||
| − | + | [[Image:pdf.png]] [[Media:Toolkit_Template_Swot_Analysis.pdf|Conducting a SWOT Analysis]] | |
| − | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 3 February 2012
| A tool that identifies the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of an organization. Specifically, SWOT is a basic, straightforward model that assesses what an organization can and cannot do as well as its potential opportunities and threats. The SWOT analysis takes the information from an environmental analysis and separate it into internal (strengths and weaknesses) and external issues (opportunities and threats). Once this is completed, the SWOT analysis determines what can be of assistance to the organization in accomplishing its objectives, and what obstacles must be minimized to achieve desired results. [1] |
|
To conduct a SWOT analysis identify the following four categories of the SWOT Matrix:
Strengths and Opportunities are identified as enhancers to desired performance, while Weaknesses and Threats are inhibitors.[2]
SWOT Matrix
Step by Step
|
Job Aid
References
- ↑ www.answers.com (20 August 2008), www.netmba.com (20 August 2008), en.wikipedia.org (20 August 2008)
- ↑ www.businessballs.com (3 October 2008), web.worldbank.org
- ↑ www.quickmba.com (13 August 2008), Wikipedia (13 August 2008), Project Cycle Management Guidelines, European Commission, 2004