Difference between revisions of "Criterion-referenced test"
From Learning and training wiki
| (One intermediate revision by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Term|CRITERION-REFERENCED TEST (CRT)|An assessment tool that helps to determine learners' [[Performance|performance]] as regards specific [[Learning Objectives|learning objectives]] or [[Competence|competencies]] that had been defined in advance. CRTs need to be composed of adequate [[Cognitivism|cognitive items]] based on predetermined learning objectives or performance statements.<ref>Criterion-referenced Test Development: Technical and Legal Guidelines for Corporate Training, Sharon A. Shrock and William C. Coscarelli. Copyright © 2007, Pfeiffer. Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.</ref> See also: [[Cognitivism]], [[Learning Objectives]], [[Performance]], [[Performance Assessment]] | + | {{Term|CRITERION-REFERENCED TEST (CRT)|An assessment tool that helps to determine learners' [[Performance|performance]] as regards specific [[Learning Objectives|learning objectives]] or [[Competence|competencies]] that had been defined in advance. CRTs need to be composed of adequate [[Cognitivism|cognitive items]] based on predetermined learning objectives or performance statements.<ref>Criterion-referenced Test Development: Technical and Legal Guidelines for Corporate Training, Sharon A. Shrock and William C. Coscarelli. Copyright © 2007, Pfeiffer. Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''See also:''' [[Cognitivism]], [[Learning Objectives]], [[Performance]], [[Performance Assessment]] | ||
| − | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | + | }} | |
| + | |||
| + | {{Tool|Developing a CRT| | ||
| + | =='''Step-by-Step'''== | ||
1. '''Analyze learning content'''<ref>''idem''.</ref> | 1. '''Analyze learning content'''<ref>''idem''.</ref> | ||
| Line 141: | Line 146: | ||
=='''Checklist for content validity of tests'''== | =='''Checklist for content validity of tests'''== | ||
Essential elements to evaluate tests’ content validity<ref>''idem''.</ref>: | Essential elements to evaluate tests’ content validity<ref>''idem''.</ref>: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 1. '''Job Analysis''' | |
| − | + | *A content validity study must include an analysis of the important work behaviors required for successful job performance. | |
| − | + | *The analysis must include an assessment of the relative importance of work behaviors and/or job skills. | |
| − | + | *Relevant work products must be considered and built into the test. | |
| − | + | *If work behaviors or job skills are not observable, the job analysis should include those aspects of the behaviors that can be observed, as well as the observed work product. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 2. '''For Tests Measuring Knowledge, Skill or Ability''' | |
| + | *The test should measure and be a representative sample of the knowledge, skill or ability. | ||
| + | *The knowledge, skill or ability should be used in and be a necessary prerequisite to performance of critical or important work behavior. | ||
| + | *The test should either closely approximate an observable work behavior, or its product should closely approximate an observable work product. | ||
| + | *There must be a defined, well-recognized body of information applicable to the job. | ||
| + | *Knowledge of the information must be a prerequisite to the performance of required work behaviors. | ||
| + | *The test should fairly sample the information that is actually used by the employee on the job, so that the level of difficulty of the test items should correspond to the level of difficulty of the knowledge as used in the work behavior. | ||
| − | + | 3. '''For Tests Purporting to Sample a Work Behavior or to Provide a Sample of a Work Product''' | |
| − | + | *The manner and setting of the test and its level and complexity should closely approximate the work situation. | |
| − | + | *The closer the content and the context of the test are to work samples or work behaviors, the stronger the basis for showing content validity.}} | |
Latest revision as of 14:51, 17 January 2014
| An assessment tool that helps to determine learners' performance as regards specific learning objectives or competencies that had been defined in advance. CRTs need to be composed of adequate cognitive items based on predetermined learning objectives or performance statements.[1]
|
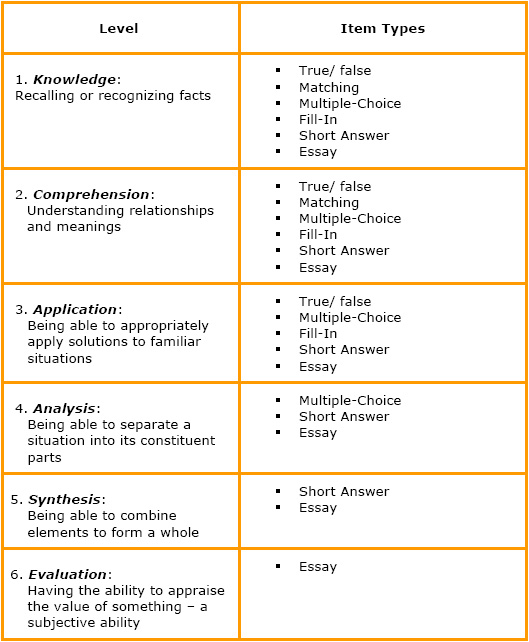
Step-by-Step1. Analyze learning content[2] Creating the learning content hierarchy is one of the most important steps in a course planning process. One of the approaches mainly used to validate a hierarchy is Bloom’s Taxonomy. Bloom’s cognitive classification consists of six levels as follows:
Note that the cognitive level needs to be defined before starting to create CRTs.
A test poses a question and either provides possible answers or distracters (called closed-ended items) or allows for a free-form response (open-ended items).
Guidelines for Writing Test ItemsGeneral guidelines
For writing the stem:
For writing the distractors:
Test length determination in seven steps: a. Have the SMEs identify the number of chapters, units, or modules that need to be assessed. b. Have the SMEs identify the objectives for each unit. c. Rate the objectives by criticality. d. Rate the objectives by domain size. e. Draw the line. f. Multiply the criticality by the domain size. g. Adjust the proportions to fit the time allotted for testing.
A checklist is created by categorizing the performance or quality of a product into specifics, of which the rater “checks” its presence or absence. Checklists are known to be more reliable because they combine a “yes” or “no” evaluation from the rater with particular behaviors or qualities. A checklist significantly reduces the rater’s required degree of subjective judgment. As a result, the level of observation errors is also reduced.
There are some minimal types of information that would help the organization make decisions surrounding the learner’s performance:
Checklist for content validity of testsEssential elements to evaluate tests’ content validity[3]: 1. Job Analysis
2. For Tests Measuring Knowledge, Skill or Ability
3. For Tests Purporting to Sample a Work Behavior or to Provide a Sample of a Work Product
|
| Below you have a list of selected websites where you can find additional information about CRT. |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| www.dsink.com | Tips for CRT checklist design. |
| www.home.sourhernct.edu | An example of a Criterion-Referenced Assessment plan for determining a child's performance in the areas of auditory memory and comprehension, formulating sentences and making inferences. |
| www.rochesterschools.com | An example of a Criterion-Referenced Assessment plan used by the Rochester School Department (USA) for assessing the district's progress in the areas of student achievement, quality of teaching and overall district performance. |
| Assessments in eLearning | This slideshow presents some of the basic concepts related to the development of good learning objectives and to the importance of measuring learning. It also presents different type of assessment. |
| Roles and Functions | This presentation outlines the roles and functions of CRT in language teaching and assessment in the Chinese context. |