Difference between revisions of "Mind Mapping"
From Learning and training wiki
| (134 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Term|MIND MAPPING|A [[Learning Methodologies| | + | {{Term|MIND MAPPING|A [[Learning Methodologies|learning methodology]] that consists of drawing [[diagrams]] to represent words, ideas, tasks, processes or other issues. It is a non-linear way of organizing information and a technique that allows to capture the natural flow of ideas about a central topic. Each idea or fact is written down and then linked by lines or curves to its major or minor (following or previous) idea or fact, thus creating a web of relationships. Its purpose is to focus attention, capturing and framing knowledge to facilitate the sharing of ideas and concepts. |
Mind maps can be used to: | Mind maps can be used to: | ||
| − | *Summarize information | + | *Summarize information and focus on the main idea(s) |
*Convey information from different sources | *Convey information from different sources | ||
*Think throught complex problems | *Think throught complex problems | ||
| − | *Present information in a format that shows the overall structure of a subject. <ref> [http://astd-cac.net astd-cac.net] (08 July 2008) [http://wikipedia.org Wikipedia](08 July 2008) [http://www.mind-mapping.co.uk www.mind-mapping.co.uk] (08 July 2008), [http://www.illumine.co.uk www.illumine.co.uk] (08 July 2008), [http://www.mindtools.com www.mindtools.com] (08 July 2008), [http://www.thinksmart.com www.thinksmart.com] (8 October 2008), | + | *Present information in a format that shows the overall structure of a subject. <ref> [http://astd-cac.net astd-cac.net] (08 July 2008) [http://wikipedia.org Wikipedia](08 July 2008) [http://www.mind-mapping.co.uk www.mind-mapping.co.uk] (08 July 2008), [http://www.illumine.co.uk www.illumine.co.uk] (08 July 2008), [http://www.mindtools.com www.mindtools.com] (08 July 2008), [http://www.thinksmart.com www.thinksmart.com] (8 October 2008), [http://www.businessdictionary.com www.businessdictionary.com] (8 October 2008)</ref> |
| + | Originally mind maps were created on paper, normally spread over a wall where people could freely write down their ideas. | ||
| − | + | Today there are several tools that allow the creation of electronic mind maps. They can be very helpful when one wants to modify an idea previously inserted or organize all the ideas in a different way or order. These [[#Practical Tips|electronic tools]] also allow that a group of people, working in different locations, contribute to the creation of mind map to address an issue of their interest. | |
| − | ==''' | + | See also: [[Data Visualization]] }} |
| − | *Take a blank paper and | + | |
| − | *Be open and have a creative attitude, trying to let ideas flow and | + | |
| − | *Free associate without limitating your ideas | + | {{Tool|Creating a Mind Map| |
| − | *Try to capture all your | + | __NOTOC__ |
| − | *Don't make any | + | =='''Step by Step'''== |
| − | + | *Determine the topic that will be the focus of your thinking. The topic should be no more then a few words. | |
| − | *Allow organization | + | *Take a blank paper - if you are using a software, open a new document - and write down the topic, wherever you want. It may be a good idea to start in the center of the paper, so as you have 360 degrees of freedom to continue your drawing. |
| − | *Experiment with different ways of linking and emphasising different aspects, | + | *To better identify and visualize the starting idea you can draw an image, using different colours. |
| + | *Be open and have a creative attitude, trying to let ideas flow and writing all of them. | ||
| + | *Free associate without limitating your ideas; you can always add new branches and add more information later on. | ||
| + | *Try to capture all your thoughts as rapidly as possible. | ||
| + | *Don't make any judgements; write everything you are thinking of. | ||
| + | *Allow organization. Once all the ideas have been added you can create links with the ones you left apart, and change the structure of your map. | ||
| + | *Experiment with different ways of linking and emphasising different aspects, e.g., using colours and highlighters. | ||
=='''Practical Tips'''== | =='''Practical Tips'''== | ||
| − | *Use single words or simple phrases | + | *Use single words or simple phrases; they can convey the same meaning of a long sentence but are more efficient. |
| − | *Use | + | *Use colours to separate different concepts; this will make the map easy to remember and will help showing the organization of the subject. |
| − | *Use symbols and images | + | *Use symbols and images; they are easier to remember than words. |
| − | *Use | + | *Use cross linkages, since information in one part of the drawing may relate with other on the other side of it. <ref>[http://www.wikihow.com www.wikihow.com] (10 October 2008), [http://www.thinkingbusiness.co.uk www.thinkingbusiness.co.uk] (10 October 2008), [http://www.mindtool.com www.mindtool.com] (10 October 2008), Tools for Knowledge and Learning, odi, 2006</ref>}} |
| + | |||
| + | =='''Job Aid'''== | ||
| + | [[Image:pdf.png]][[Media:Toolkit_Template_Mind_Mapping.pdf| Creating a Mind Map]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{addtitle}} | ||
| + | {{Termaddition|Below you have a selected compilation of electronic tools that allow the creation of mind maps. All the tools listed are free, available on the Internet. For each tool listed some general information is provided : on-line or desktop use; special features available; and degree of flexibility when constructing the map. Click on the image on last column (visualization) to see a sample of the type of map each tool allows you to create. | ||
| − | { | + | UNITAR is using VUE on a process mapping exercise.}} |
| − | + | {|border=1 | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | !Tools | |
| + | !Type of Application | ||
| + | !Special Features | ||
| + | !Structure | ||
| + | !Visualization | ||
| + | |- | ||
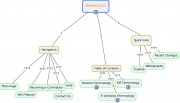
| + | |[http://freemind.sourceforge.net/wiki/index.php/Main_Page Freemind] | ||
| + | |To download | ||
| + | (1,51 KB) | ||
| + | |Link to files and web-sites | ||
| + | |Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | ||
| + | |[[Image:freemind.jpeg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
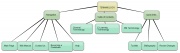
| + | |[http://cmap.ihmc.us CMAP Tools] | ||
| + | |To download | ||
| + | (1,62 KB) | ||
| + | |Link to files and web-sites | ||
| + | |Free structure; but every arrow connecting two nodes must contain a label | ||
| + | |[[Image:Cmap_Tools.jpg|thumb]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.mindmeister.com Mindmeister] | ||
| + | |On-line. Two versions: Basic for free, | ||
| + | Premium to pay (4$ per month) | ||
| + | |Link to files and web-sites | ||
| + | |Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | ||
| + | |[[Image:mindmeister.jpg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://bubbl.us Bubbl.us] | ||
| + | |On-line | ||
| + | |Link to web-sites | ||
| + | |Free structure | ||
| + | |[[Image:bubble.us.jpg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
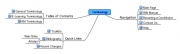
| + | |[http://vue.tufts.edu VUE] | ||
| + | |To download | ||
| + | (1,51 KB) | ||
| + | |Link to files and web-sites | ||
| + | |Free structure. Possibility two add a label on the connection between two nodes. | ||
| + | |[[Image:VUE.jpeg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://compendium.open.ac.uk/institute Compendium] | ||
| + | |To download | ||
| + | (1,58 KB) | ||
| + | |Link to files and web-sites | ||
| + | |Free structure; but every node has to belong to a category (question, decision, argument, idea, etc.) | ||
| + | |[[Image:Compendium.jpg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.wisemapping.com Wisemapping] | ||
| + | |On-line | ||
| + | |Link to web-sites | ||
| + | |Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | ||
| + | |[[Image:Wisemapping.jpg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.mind42.com Mind42] | ||
| + | |On-line | ||
| + | |Link to web-sites | ||
| + | |Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | ||
| + | |[[Image:Mind42.png|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
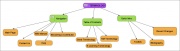
| + | |[http://freeplane.sourceforge.net/ Freeplane] | ||
| + | |To download | ||
| + | (22,7 MB) | ||
| + | |Link to files and web-sites | ||
| + | |Free structure; a growing set of node extensions provide for details, metadata, images, hyperlinks. | ||
| + | |[[Image:FreeplaneFunctions.jpg|thumb|]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {{Addlink|Below is an additional resource for mind map templates and e-books:}} | ||
| + | {|border=1 | ||
| + | !Link | ||
| + | !Content | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.mindmapinspiration.co.uk/#/templates-mind-map/4520968403 Mind Map Inspiration] | ||
| + | |This resource provides access to a number of mind map templates. Additionally, links are available to some free e-books on using mind maps and a gallery of mind maps to browse through. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.rcfouchaux.ca/blog/2013/01/19/mind-mapping-for-instructional-design/ Mind mapping for instructional design] | ||
| + | |This article highlights the importance of Mind Mapping tools in playing an increasingly role in the design, planning and implementation of learning experiences. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.datavizcatalogue.com/methods/brainstorm.html Brainstorm/Mind Maps] | ||
| + | |This entry of the Data Visualisation Catalogue explains what are mindmaps and how to create one. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.pinterest.com/click4it/mind-mapping/ Pinterest Board on Mind Mapping] | ||
| + | (Infographics) | ||
| + | |Check out Click4it's Pinterest Board on Mind Mapping and visualize it! | ||
| + | |} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:58, 3 February 2014
| A learning methodology that consists of drawing diagrams to represent words, ideas, tasks, processes or other issues. It is a non-linear way of organizing information and a technique that allows to capture the natural flow of ideas about a central topic. Each idea or fact is written down and then linked by lines or curves to its major or minor (following or previous) idea or fact, thus creating a web of relationships. Its purpose is to focus attention, capturing and framing knowledge to facilitate the sharing of ideas and concepts.
Mind maps can be used to:
Originally mind maps were created on paper, normally spread over a wall where people could freely write down their ideas. Today there are several tools that allow the creation of electronic mind maps. They can be very helpful when one wants to modify an idea previously inserted or organize all the ideas in a different way or order. These electronic tools also allow that a group of people, working in different locations, contribute to the creation of mind map to address an issue of their interest. See also: Data Visualization |
Step by Step
Practical Tips
|
Job Aid
| Below you have a selected compilation of electronic tools that allow the creation of mind maps. All the tools listed are free, available on the Internet. For each tool listed some general information is provided : on-line or desktop use; special features available; and degree of flexibility when constructing the map. Click on the image on last column (visualization) to see a sample of the type of map each tool allows you to create.
|
| Tools | Type of Application | Special Features | Structure | Visualization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freemind | To download
(1,51 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| CMAP Tools | To download
(1,62 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure; but every arrow connecting two nodes must contain a label | |
| Mindmeister | On-line. Two versions: Basic for free,
Premium to pay (4$ per month) |
Link to files and web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| Bubbl.us | On-line | Link to web-sites | Free structure | |
| VUE | To download
(1,51 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure. Possibility two add a label on the connection between two nodes. | |
| Compendium | To download
(1,58 KB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure; but every node has to belong to a category (question, decision, argument, idea, etc.) | |
| Wisemapping | On-line | Link to web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| Mind42 | On-line | Link to web-sites | Ramification only horizontal. No freedom to change the structure; information always presented on left and right hand. | |
| Freeplane | To download
(22,7 MB) |
Link to files and web-sites | Free structure; a growing set of node extensions provide for details, metadata, images, hyperlinks. |
| Below is an additional resource for mind map templates and e-books: |
| Link | Content |
|---|---|
| Mind Map Inspiration | This resource provides access to a number of mind map templates. Additionally, links are available to some free e-books on using mind maps and a gallery of mind maps to browse through. |
| Mind mapping for instructional design | This article highlights the importance of Mind Mapping tools in playing an increasingly role in the design, planning and implementation of learning experiences. |
| Brainstorm/Mind Maps | This entry of the Data Visualisation Catalogue explains what are mindmaps and how to create one. |
| Pinterest Board on Mind Mapping
(Infographics) |
Check out Click4it's Pinterest Board on Mind Mapping and visualize it! |
References
- ↑ astd-cac.net (08 July 2008) Wikipedia(08 July 2008) www.mind-mapping.co.uk (08 July 2008), www.illumine.co.uk (08 July 2008), www.mindtools.com (08 July 2008), www.thinksmart.com (8 October 2008), www.businessdictionary.com (8 October 2008)
- ↑ www.wikihow.com (10 October 2008), www.thinkingbusiness.co.uk (10 October 2008), www.mindtool.com (10 October 2008), Tools for Knowledge and Learning, odi, 2006